Explanation | |
A standard image file format for Windows. Most Windows programs, including word processing programs, can read images in this format. | |
A compressed file format in which the compression level can be selected. The JPEG format lets you highly compress image data. However, the higher the compression, the lower the image quality. Any lost image quality data cannot be restored, and the quality deteriorates each time the data is saved. The TIFF format is recommended when modification and retouching are required. | |
A TIFF format where multiple pages are saved to the same file. You can also edit the scanned images before saving them. See Epson Scan Help for details. To open Multi-TIFF files, you need a program that supports it. | |
A document format that can be read on both Windows and Macintosh systems (platform independent). To use PDF documents in Windows, you need Adobe Reader or Acrobat. Multi-page documents can be saved as one PDF file. When you save color or grayscale images in PDF, you can select a compression level. You can also edit the scanned images before they are saved. See Scanning Directly to a PDF File for details. | |
A standard image file format for Macintosh. Most Macintosh programs, including word processing programs, can read images in this format. | |
PRINT Image Matching II JPEG (*.JPG) or TIFF (*.TIF) | A file format that includes PRINT Image Matching II data for enhanced quality and a wider color range. Print Image Matching II compatible printers can then print this data for brilliant, true-to-life results. (PRINT Image Matching data does not affect the way the image displays on the screen.) Available in JPEG or TIFF format. |
A file format created for exchanging data between many programs, such as graphic and DTP software. When scanning black & white images, you can specify the compression type. |
Click the Preview button toward the bottom of the Epson Scan window. The ADF loads your first document page, then Epson Scan prescans it and displays it in the Preview window. The ADF then ejects your first page. Place your first page on top of the rest of. Follow the step-by-step instructions here to scan your originals using any of the available scanning methods. Scanning in Full Auto Mode. Scanning in Home Mode. Scanning in Office Mode. Scanning in Professional Mode. Previewing and Adjusting the Scan Area. Various Types of Scanning.


Scanning Using Epson Printer
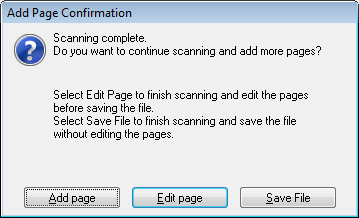
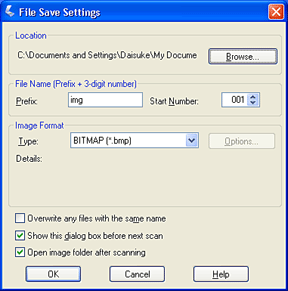
Scan With Epson
Explanation | |
A standard image file format for Windows. Most Windows programs, including word processing programs, can read images in this format. | |
A compressed file format in which the compression level can be selected. The JPEG format lets you highly compress image data. However, the higher the compression, the lower the image quality. Any lost image quality data cannot be restored, and the quality deteriorates each time the data is saved. The TIFF format is recommended when modification and retouching are required. | |
A TIFF format where multiple pages are saved to the same file. You can also edit the scanned images before saving them. See Epson Scan Help for details. To open Multi-TIFF files, you need a program that supports it. | |
A document format that can be read on both Windows and Macintosh systems (platform independent). To use PDF documents in Windows, you need Adobe Reader or Acrobat. Multi-page documents can be saved as one PDF file. When you save color or grayscale images in PDF, you can select a compression level. You can also edit the scanned images before they are saved. See Scanning Directly to a PDF File for details. | |
A standard image file format for Macintosh. Most Macintosh programs, including word processing programs, can read images in this format. | |
PRINT Image Matching II JPEG (*.JPG) or TIFF (*.TIF) | A file format that includes PRINT Image Matching II data for enhanced quality and a wider color range. Print Image Matching II compatible printers can then print this data for brilliant, true-to-life results. (PRINT Image Matching data does not affect the way the image displays on the screen.) Available in JPEG or TIFF format. |
A file format created for exchanging data between many programs, such as graphic and DTP software. When scanning black & white images, you can specify the compression type. |