- Practice Velocity Problems
- Practice Velocity Download
- Practice Velocity And Docutap Merger
- Practice Velocity Pvm Login
Get up to speed as quickly as possible. Remember, we are still practicing HS. Playing so fast that you start to feel stress and make mistakes will not improve technique because you are just practicing mistakes and acquiring bad habits. Forcing the fingers to play the same way faster is not the way to increase speed. As demonstrated with parallel play, you need new ways that automatically increase speed and reduce stress. In fact, with parallel play, it is often easier to play fast than slowly. Devise hand positions and motions that automatically increase speed; this topic is one of the major contributions of this book, and will be treated topic by topic later on as it is too big to be covered here; it involves such specific skills such as thumb-over method, glissando motion, relaxation, flat finger positions, arm and wrist motions, etc., and the use of 'post practice improvement'. If you do not make significant progress in a few minutes, you are probably doing something wrong -- think of something new. Students who use the intuitive method are resigned to repeating the same thing for hours with little visible improvement. That mentality must be avoided in order to learn faster. There are two types of situations you will encounter when increasing speed. One involves technical skills you already have; you should be able to bring these up to speed in minutes. The other involves new skills; these will take longer and will be discussed in section 15 below.
NWTG Nike Velocity 2.0 Practice Men’s Football Jersey Shirt White 659179 XL. Condition is New with tags. Shipped with USPS First Class Package. Over 800 urgent care centers in 50 states have turned to Practice Velocity for multiple software solutions (including EMR and practice management), contracting, credentialing and billing services. Practice: Position, velocity and acceleration. This is the currently selected item. Vector addition. Practice: Velocity and acceleration vectors. Understanding net forces. Practice: Net forces. Force and acceleration. Practice: Applying gravity to a particle. Particle collisions. Average velocity. Velocity is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time. Velocity is a vector, which means the problem should be solved graphically. Draw an arrow pointing toward the top of the page (north). Draw another arrow to the left.
Technique improves most rapidly when playing at a speed at which you can play accurately. This is especially true when playing HT (please be patient -- I promise we will eventually get to HT practice). Since you have more control HS, you can get away with much faster play HS than HT without increasing stress or forming bad habits. Thus it is erroneous to think that you can improve faster by playing as fast as possible (after all, if you play twice as fast, you can practice the same passage twice as often!). Since one major objective of HS practice is to gain speed, the need to attain speed quickly and to practice accurately become contradictory. The solution is to constantly change the speed of practice; do not stay at any one speed for too long. For very difficult passages that require skills you don't already have, there is no alternative but to bring the speed up in stages. For this, use speeds that are too fast as exploratory excursions to determine what needs to be changed in order to play at such speeds. Then slow down and practice those new motions.
To vary the speed, first get up to some manageable 'maximum speed' at which you can play accurately. Then go faster (using parallel sets, etc., if necessary), and take note of how the playing needs to be changed (don't worry if you are not playing accurately at this point because you are not repeating it many times). Then use that motion and play at the previous 'maximum accurate speed'. It should now be noticeably easier. Practice at this speed for a while, then try slower speeds to make sure that you are completely relaxed and absolutely accurate. Then repeat the whole procedure. In this way, you ratchet up the speed in manageable jumps and work on each needed skill separately. In most cases, you should be able to play most of the new piece, at least in small segments, HS, at the final speed during the first sitting. In the beginning, getting up to speed at the first sitting may seem unattainable but, with practice, every student can reach this objective surprisingly quickly.
Overview
Question of the Day: How can programming languages hide complicated patterns so that it is easier to program?
After a brief review of how they used the counter pattern to move sprites in previous lessons, students are introduced to the idea of hiding those patterns in a single block. Students then head to Code Studio to try out new blocks that set a sprite's velocity directly, and look at various ways that they are able to code more complex behaviors in their sprites.
Purpose
This lesson launches a major theme of the chapter: that complex behavior can be represented in simpler ways to make it easier to write and reason about code.
In this lesson students are taught to use the velocity blocks to simplify the code for moving a sprite across the screen. This marks a shift in how new blocks are introduced. Whereas previously blocks were presented as enabling completely new behaviors, they are now presented as simplifying code students could have written with the blocks previously available. Over the next several lessons, students will see how this method of managing complexity allows them to produce more interesting sprite behaviors.
Assessment Opportunities
Use the velocity and rotationSpeed blocks to create and change sprite movements
See Level 10 in Code Studio. (Level 6 can be used to check rotationSpeed.)
Describe the advantages of simplifying code by using higher level blocks
In the wrap up, check students' descriptions of the blocks that they would create and why they would want to create them.
Agenda
Lesson Modifications
Warm Up (5 min)
Activity (30 min)
Wrap Up (5 min)
View on Code Studio
Objectives
Students will be able to:
- Use the velocity and rotationSpeed blocks to create and change sprite movements
- Describe the advantages of simplifying code by using higher level blocks
Links
Heads Up! Please make a copy of any documents you plan to share with students.
For the Teachers
- Velocity - Slides
Introduced Code
Lesson Modifications
Attention, teachers! If you are teaching virtually or in a socially-distanced classroom, please see these modifications for Unit 3.
Warm Up (5 min)
Demonstrate: Ask for a volunteer to come to the front of the class and act as your 'sprite'. Say that you will be giving directions to the sprite as though you're a Game Lab program.
When your student is ready, face them so that they have some space in front of them and ask them to 'Move forward by 1'. They should take one step forward. Then repeat the command several times, each time waiting for the student to move forward by 1 step. You should aim for the repetitiveness of these instructions to be clear. After your student has completed this activity, have them come back to where they started. This time repeat the demonstration but asking the student to 'Move forward by 2' and have the student take 2 steps each time. Once the student has done this multiple times ask the class to give them a round of applause and invite them back to their seat.
Prompt: I was just giving instructions to my 'sprite', but they seemed to get pretty repetitive. How could I have simplified my instructions?
Discussion Goal
Goal: The earlier demonstration should have reinforced the fact that repeatedly giving the same instruction is something you would never do in real life. You would instead come up with a way to capture that the instruction should be repeated, like 'keep moving forward by 1.'
Discuss: Give students a minute to write down thoughts before inviting them to share with a neighbor. Then have the class share their thoughts. You may wish to write their ideas on the board.
Remarks
Programming languages also have ways to simplify things for us. Today, we're going to look at some blocks in Game Lab that hide complicated coding patterns to make things easier for programmers.
Question of the Day: How can programming languages hide complicated patterns so that it is easier to program?
Activity (30 min)
Remarks
One way to simplify these instructions is to just tell our 'sprite' to keep moving by 1 or 2, or however many steps we want. As humans, this would make instructions easier to understand, and as we're about to see there's a similar way to make our code simpler as well.
Transition: Move students to Code Studio
Circulate: These levels introduce the velocityX, velocityY, and rotationSpeed properties that you just discussed with students. Check in with students to see how they are doing and keep track of when everyone has made it to the end of level 10.
Wrap Up (5 min)
Journal
Assessment Opportunity
As students describe the blocks that they would make, ensure that they are relating the specific code that a block would use to the higher-level concept of what it would do. For example, a 'velocity' block would move a sprite across the screen, and it would include blocks that use the counter pattern on a position property.
Students should describe the advantages of having these blocks, such as not needing to re-write the code all the time, or making it easier to read what the program is doing.
Prompt: You learned a few new blocks today. At first glance, these blocks did the same sorts of things we'd already done with the counter pattern, but made it simpler for us to do them. As you went through the puzzles, though, you started doing some interesting movements that we hadn't been able to do before.
- Describe one of those movements, and how you made it.
- Describe another block that you'd like to have.
- What would you name it?
- What would it do?
- What code would it hide inside?
- How would it help you?
Remarks
All of the movements that we did today are possible without the new blocks, but it would be very complicated to code them. One of the benefits of blocks like velocity is that when we don't have to worry about the details of simple movements and actions, we can use that extra brainpower to solve more complicated problems. As you build up your side scroller game, we'll keep looking at new blocks that make things simpler, so we can build more and more complicated games.
- Lesson Overview
- (click tabs to see student view)
- Skill Building
- (click tabs to see student view)
Student Instructions
One way to move sprites in Game Lab is with the counter pattern. For example sprite1.x = sprite1.x + 1 moves a sprite by 1 pixel each frame of the draw loop. This pattern is so common that sprites have a velocityX property that does this for you.
- Drag a
sprite.velocityXblock directly below where your sprite is created. ( Show me where ) - Write the name of your sprite in the block.
- Assign the
velocityXproperty a value of 1. - Run the code. What happens?
- Re-run the code giving the
velocityXproperty a different value. What's changing?
- Video: Velocity
- (click tabs to see student view)
Teaching Tip
Discussion Goals
It may not be obvious to students why the velocity block is so powerful. The immediate answer is that the velocity block allows a programmer to set the velocity at the beginning of the program and not have to worry about the counter pattern inside the draw loop (as Game Lab will take care of that). If students are having trouble of thinking of situations in which the velocity block provides a big advantage, assure them that they will tackle some problems in the coming lesson that they will need this block for.
As students give you examples, try to elicit answers that use both positive and negative numbers, and that use the x and y positions as well as sprite rotation.
Student Instructions
Questions to Consider
- Why might you want to use a velocity block instead of the counter pattern?
- Give an example of a counter pattern and how you could use a velocity block instead.
- Skill Building
- (click tabs to see student view)
Student Instructions
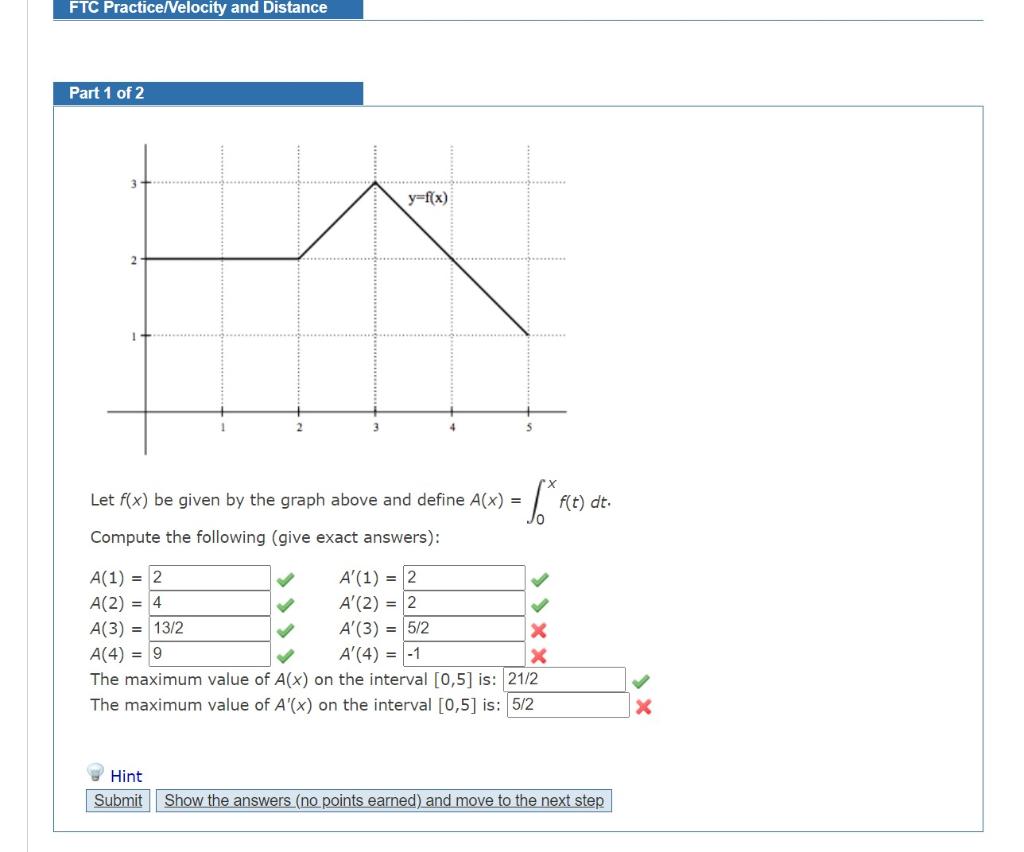
Here is a feather sprite that should be floating down the screen. If velocityX makes a sprite move to the right, can you find the block that will make the feather move down?
Find the block that will make the feather sprite go down the screen, and use it outside the draw loop. ( Show me where )
View on Code StudioStudent Instructions
You can use rotationSpeed to make your sprites spin. If you want your sun to rotate by two degrees each time it's drawn, you can use sun.rotationSpeed = 2 before the draw loop, after you create your sprite.
Make the sun rotate by 3 degrees each time using the rotationSpeed block. ( Show me where )
Teaching Tip
This is a good time to remind students that code outside the draw loop is used to set up the program. It is for how you want your program to start. Code inside the draw loop is for things that are changing as the program is running, user interaction.
There may be some confusion that the new blocks are animation (changing position) and yet have gone outside the draw loop up until this point. That is because up until this point, the velocity has been set at the beginning of the program and not changed. When students want the velocity to change during the program, it will need to go inside the draw loop.
Student Instructions
You used rotationSpeed outside the draw loop to make your sprite rotate when your program started. You can also use rotationSpeedinside the draw loop to change the speed of the sprite during the game. For example, a sprite can start rotating when the user presses the space bar, and it will keep rotating until it's told to stop.
- Look at the
ifstatement inside the draw loop that checks whether the space bar has been pressed. ( Show me where ) - Use the
rotationSpeedblock to make the color wheel start spinning when the user presses the space bar.
Student Instructions
One advantage to using the velocity blocks inside conditionals (if blocks) is that your sprite keeps moving, even after the condition stops being true. For example, you only had to press a key once to start the color wheel spinning, and it kept spinning forever. The code below uses if statements to make a fish sprite move in different directions.
- Look at
ifstatements that check the sprite's position and set its velocity. - With your partner, discuss what you think the code will do, and write your answer below.
- Once you have submitted your answer, run the code.
Student Instructions
This ball bounces back when it hits the bottom of the screen. Can you make it bounce back when it hits the top of the screen?
- Run the code and see how it works.
- Look at how conditionals and velocity are used to make the ball bounce at the bottom of the screeen.
- Add code to make the ball bounce at the top of the screen.
- Velocity Practice
Practice using the velocity blocks with these activities.
Choose from the following activities:
Make the robot fly once the space bar has been pressed at least once.
Dip the paint brush in the paint.
View on Code StudioStudent Instructions
For this animation, you'll help the 'Flybot' to take off. It should start moving up when the space bar is pressed, and it should continue moving up even after the space bar is released.
- Use an
ifstatement inside the draw loop to check when the space bar is pressed. - Use the
velocityYblock to make the sprite move up when the user presses the space bar. - Check that your animation behaves the way you'd expect.
Student Instructions
Dip the paintbrush in the paint.
- Use a conditional to send the paint brush down if the down arrow is pressed.
- Use a different conditional to send the paint brush up if it reaches the palette.
- Hint: You will need to check its y property.
- Assessment
- (click tabs to see student view)
Assessment Opportunities
Key Concepts:
Use conditionals to control the flow of a program; model two dimensional movement on a coordinate plane.
Assessment Criteria:The fish swims to the right side of the screen, turns and swims to the left side of the screen, then repeats. The sprite appears to face the appropriate direction at all times. There are no extra blocks in the program, and the counter pattern is not used.
The fish swims to the right side of the screen, turns and swims to the left side of the screen, but perhaps does not face the right direction while moving. The counter pattern is not used.
The fish swims to the right side of the screen, turns and swims to the left side of the screen, but does not repeat. The student only changed its velocity by using the provided first conditional statement.
The fish just moves right across the screen, then disappears.
Student Instructions
The code below should make the fish start moving right as soon as you press 'Run'. Using conditional statements and the .velocity block, you can make it continually swim back and forth.
Look at the three
ifstatements inside the draw loop.Use a
sprite.velocityXblock inside eachifstatement to make the three following movements:- If the user presses the right arrow key, move the fish to the right.
- If the fish gets to the right-hand side of the screen, move the fish to the left.
- If the fish gets to the left-hand side of the screen, stop the fish.
- Velocity Challenges
Practice Velocity Problems
View on Code StudioTry out these new blocks and challenges with velocity.
Practice Velocity Download
Choose from the following activities:
Can you change velocities four separate times?
None
View on Code StudioStudent Instructions
Study the animation to the right. Notice that the purple alien sprite changes between x and y velocities when it is near each corner of the screen.
- Run the program and to understand how it works so far.
- Add
.velocityXand.velocityYblocks to each conditional to make the alien complete the full circuit.
Be careful! If the sprite starts moving diagonally, it might mean it has both an x and y velocity. In the first corner the alien needs to stop moving up and start moving right.
View on Code StudioStudent Instructions
Use what you've learned to create whatever you like. When you're finished, you can click to send your creation to a friend, or to send it to your Projects Gallery.
Standards Alignment
View full course alignment
Practice Velocity And Docutap Merger
CSTA K-12 Computer Science Standards (2017)
- 2-AP-11 - Create clearly named variables that represent different data types and perform operations on their values.
- 2-AP-12 - Design and iteratively develop programs that combine control structures, including nested loops and compound conditionals.
- 2-AP-13 - Decompose problems and subproblems into parts to facilitate the design, implementation, and review of programs.
- 2-AP-16 - Incorporate existing code, media, and libraries into original programs, and give attribution.
- 2-AP-17 - Systematically test and refine programs using a range of test cases.
- 2-AP-19 - Document programs in order to make them easier to follow, test, and debug.
Open Questions
Practice Velocity Pvm Login
- Is more clarification needed to run the warm-up demonstration? Does this activity actually help scaffold the introduction of the velocity blocks?